Table of Contents
WHAT IS VITAMIN D, AND WHAT IS IT FOR?
Vitamin D is an essential substance for our health; its primary functions are maintaining bone health and the immune system.
According to the NHS UK, this vitamin is directly related to strong bones, increases calcium absorption at the intestinal level, and acts at muscular, nervous and immune levels.
Despite this, it is still a cause for concern as a large part of the population is vitamin D deficient.
Some of these ideas may already be on your mind, but you probably didn’t know that medicinal mushrooms are one of the world’s best natural sources of vitamin D. Here’s why.
TYPES OF VITAMIN D
First, it is essential to differentiate between two fundamental forms that require the action of the liver and kidneys to be biologically active.
ERGOCALCIFEROL (D2)
It is mainly of plant origin. It is incorporated into the diet through the consumption of plant foods containing it, such as medicinal mushrooms and, more specifically, food supplements made from them in powder and extract form. The immune system supplement Bio-Defense would be a good example, incorporating Reishi, Shiitake, Maitake, oyster mushroom and king oyster mushroom powder.
CHOLECALCIFEROL (D3)
Unlike the former, it is found in the skin after exposure to UV radiation, but it can also be obtained from the diet, mainly from foods of animal origin.

FOODS RICH IN VITAMIN D
According to various publications, few natural foods contain Vitamin D. These include oily fish such as salmon, tuna and mackerel, but also some vegetables and mushrooms and fungi.
In this respect, studies with D2 obtained from mushrooms and fungi have shown an increase in 25OHD (circulating vitamin D) in clinical trials in healthy people who are deficient in winter. After two weeks, serum 25OHD was significantly higher in the mushroom vitamin D group than in the placebo group.
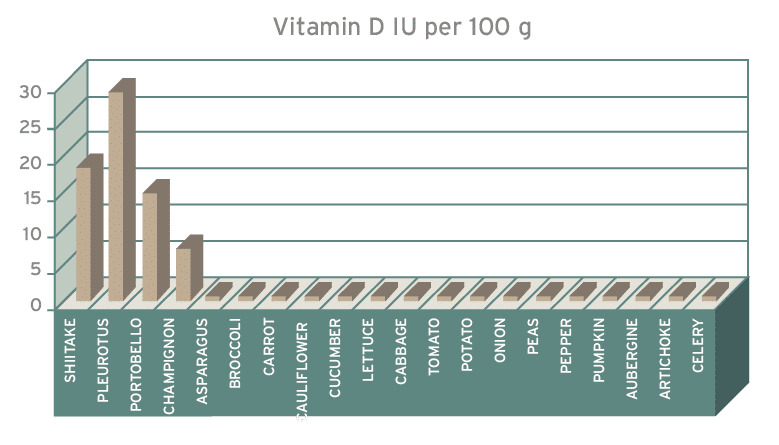
FRUITS, VEGETABLES AND MEDICINAL MUSHROOMS
According to the study cited above and the graph above, there is no longer any doubt: medicinal mushrooms are a good source of vitamin D. The most prominent in this respect are Shiitake, Maitake and Pleurotus ostreatus, among others. They all have vitamins B, C and E, and D precursors.
QUALITY SOURCES OF VITAMIN D
Mushrooms are an excellent source of vitamin D if they have been cultivated sustainably with non-invasive techniques, follow ecological production and assurance requirements and receive solar radiation. Like us, they need UV radiation to synthesise this vitamin properly.
Lee’s research group (Lee G et al., 2009) studied the nutritional and therapeutic differences between Shiitake grown with and without UV radiation, showing that Shiitake grown under optimal radiation conditions had significantly higher levels of this vitamin and more calcium than Shiitake grown indoors.
HOW TO INCREASE VIT D QUICKLY
It is estimated that between 80% and 90% of our body’s reserves of this vitamin come from exposure to the sun. At the latitudes where we live, reserves of this vitamin could be guaranteed by exposing our faces and arms to the sun for 5 to 15 minutes, preferably in the central hours of the day. However, this is a general estimate as air pollution and clouds influence vitamin D absorption in addition to latitudes and times of the day.

SYMPTOMS OF VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY
As we have already mentioned, vitamin D, should be considered a prohormone, as it is converted into a metabolite that acts as a steroid hormone essential for maintaining skeletal homeostasis by regulating calcium and phosphorus levels (Deluca et al. 1990). For this reason, it is the vitamin par excellence when it comes to skeletal mineralisation, i.e. the maintenance of adequate bone health throughout our lives.
BONES AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
Rickets and bone softening are consequences of VitD deficiency. Still a lack of this vitamin in the blood has also been linked to numerous chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, cancer and other diseases affecting the nervous system, such as depression.
Numerous studies have shown an anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic, even anti-metastatic capacity in cancerous processes such as breast and kidney cancer.
This anti-tumour capacity has aroused clinical interest, but vitamin D has no therapeutic application due to its high calcium action. Direct administration at supraphysiological doses induces hypercalcaemia.
However, further studies are needed to establish clear links between this vitamin and the development of specific pathologies.
THE SUNSHINE VITAMIN
Vitamin D3 synthesis occurs several hours after sun exposure. When sun exposure is continuous, levels of the vitamin are modulated by the synthesis of melanin, the main competitor of vitamin D3.
This allows our body to regulate excessive production during prolonged periods of sun exposure.
Indeed, our body’s health depends on balanced sun exposure. Excessive and unprotected exposure generates breaks in genetic material that trigger carcinogenic processes and, increased pigmentation can decrease vitamin D3 production by up to 50 times (Clements et al. 1992).
In contrast, complete protection prevents UV radiation from reaching the dermis, ultimitely inhibiting the main synthesis pathway of the anti-tumour hormone vitamin D.
IN SUMMARY…
- Despite our country’s daylight hours, a recent study shows that 75% of the population is reported to have low levels of vitamin D, which rises to 80% in young people.
- This vitamin is related to immune system function, mental balance, bone health and the incidence of certain viruses.
- Maintaining adequate levels of vitamin D protects us from immune problems and helps us to grow and develop bones and maintain our mental balance.
- Looking for a natural supplement containing vitamin D? At Hifas da Terra we have developed Bio-Defense, the daily support for the body’s defences with bioactive substances from the most studied medicinal mushrooms.
We recommend

How to Obtain More Energy and Fight Fatigue Naturally
If you’ve been feeling mentally and physically exhausted, struggling to focus, or asking yourself, Why am I so fatigued?, you’re not alone. Fatigue is a

Healthy and active brain, what science has already proven and you should know
How to keep the brain healthy and young despite the passing years? Recent research on super seniors ーoctogenarians whose cognitive characteristics are those of people